injection diesel-mecanique -
Diesel: Self-Ignition Engine Sucks in Air and Strongly compresses
Diesel principle
Power circuit
Preheating circuit
Injection pumps
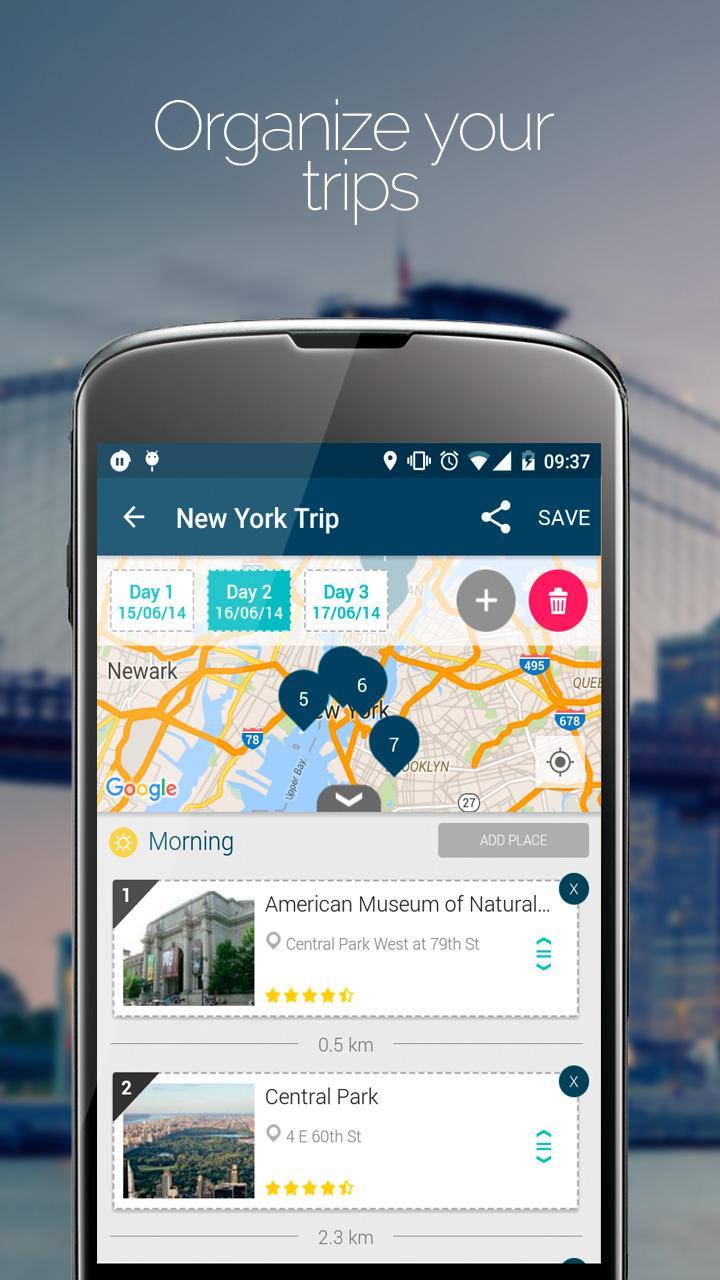
TP 1: Periodic interviews with the diesel engine
TP 2: repair the diesel power circuit
TP 3: Disassembly, control, repair, assembly and adjustment of an injector
TP 4: Check and repair the cold starting circuit
TP 5: Remove and rest the injection pump
TP 6: controls and settings
Diesel injection system
Diesel injection system
- Control on the different elements of a rotary injection pump;
- Disassembly and reassembly of a rotary injection pump
- Questions and problems
- Real or simulated cases or representative vehicles
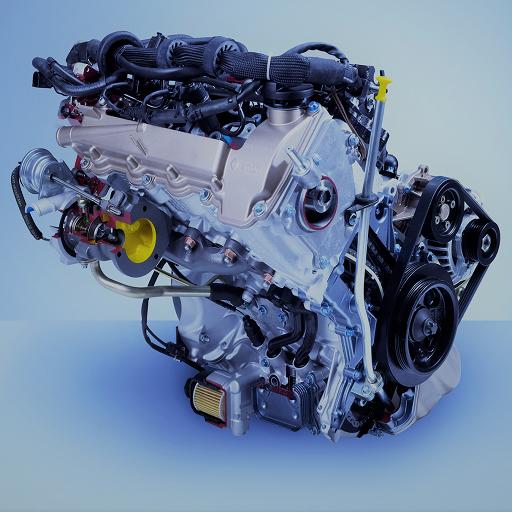
The diesel engine is a self-turnout engine that only aspires air and compresses it strongly. This process makes it possible to obtain compression significantly higher than that of the fuel engine sensitive to rattling and using a mixture of air and fuel and a controlled ignition.
Characteristics of a diesel engine
Advance at the opening of the admission (AOA)
Delay when closing the admission (RFA)
Ignition advance (AA)
Advance at the opening of the exhaust (AOE)
Delay in the exhaust closure (RFE)
Real diagram
Advantage of the diesel engine
Diesel engine disadvantages
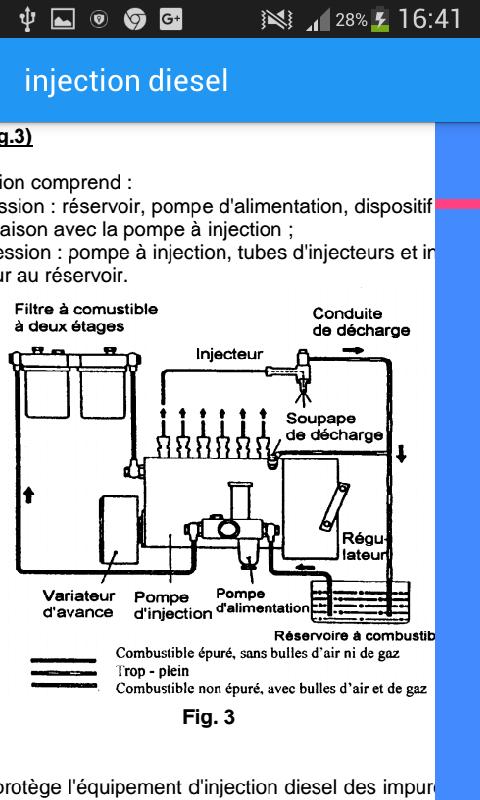
Power circuit
Fuel filter
Power pump
Injection pump
Cruise control
Advanced
Discharge pipe
Injectors
Different types of power circuits
Power circuit with online pump
"Suction" circuit
"Low pressure" circuit
Power circuit with distributor pump
air filter
Diesel filter
Filters with priming pump
Piping
Food pumps
Main types of food pumps
Membrane pump
Pump
Simple effect pump
Transfer phase
By turning, the camshaft of the injection pump leads the eccentric (1) in the high position. The piston (4) is pushed up by the pebble (2) and the stem (3). The displacement of the piston causes the valve closure (6) under the effect of the pressure of the fuel in the room (7), the valve (8) deviates from its seat, the diesel contained in the room (7) flows to the room (9) It is the transfer phase.
Self -regulator
The flow of the power pump being higher than the flow repressed by the injection pump, there is a time when the pressure in the room (9) is equal to the pressure of the spring (5) on the piston (4); This can no longer move, there is no longer any aspiration or repression: this is the self-regulating phase. Recall that the roller (2) is still in contact with the eccentric (1) via a recall spring not appearing on the diagram.
Left aspiration. In the center: Transfer phase. Right: self -regulating phase.
1. Excentrics on the camshaft of the injection pump; 2.Galet; 3.tige; 4.piston; 5. Resort; 6.A intake; 7. Chamber; 8.Clapet of discharge; 9. Transfer chamber.
1. Excentrics on the camshaft of the injection pump; 2.Galet; 3 .tige; 4.Indessing admission; 5.piston; 6. Chamber of admission; 7. 8. Compression chamber; 9. Resort; 10.Clapet of discharge; 11. Chamber; 12. Retraisal valve; 13. Transfer bed
Injectors
Injectors types
a) Injector with nipple and strangulation b) holes injector.
1. Arrivée, 2.Corps-support, 3. Fixing, 4. Intermediate Disk, 5. Injector, 6.Crou-Rraccord de Retoulement, 7.Filtre-Tige, 8.Canai for recovery of leaks, 9.rondelles of tape, 10. Retoulation level, 11.ressort, 12.Tige-pose, 13.
Types of injectors.
a) Netherlands injector and strangulation,
b) Holes injector.
1. Pressure stretch, 2. injector corps,
3. Injector help, 4.
5. Compression chamber, 6.
7. injection stretch, 8.
ofppt trem